Heaps
A Heap is a special Tree-based data structure in which the tree is a complete binary tree. Generally, Heaps can be of two types:
1. Min Heap
2. Max Heap
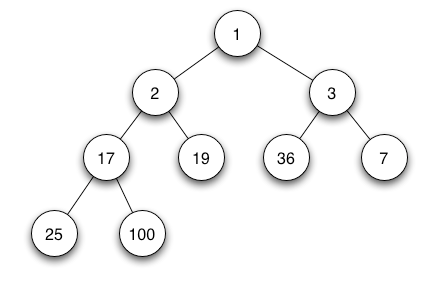
Min Heap
In a Min-Heap the key present at the root node must be minimum among the keys present at all of it’s children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
Implementation
Min Heap can be Implemented using arrays or it can be implemented using doubly linked list
Array Implementation
Max Heap
In a Max-Heap the key present at the root node must be greatest among the keys present at all of it’s children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
Implementation
Max Heap can be Implemented using arrays or it can be implemented using doubly linked list
Array Implementation
Problem on Heaps
Work on some problems to get know more about heaps.
Heaps